Building Jenkins Freestyle Project: Python Unit Test for Website Loading Verification
Introduction
In my previous article, we explored the installation and setup process of Jenkins on a server. Now, in this write-up, we will delve into the practical aspects of utilizing Jenkins' freestyle build job to create a Python unit test that establishes a connection with a website. The primary objective of this unit test is to determine the success or failure of the website loading process.
Setting up the Environment
First, we need to install some applications and packages on the system that hosts Jenkins.
Chrome Browser(google-chrome)
## download the Google Linux package signing key and add it to the system's list of trusted keys. wget -q -O - https://dl.google.com/linux/linux_signing_key.pub | sudo apt-key add - ## download the Google Chrome stable version package for the AMD64 architecture sudo add-apt-repository "deb http://dl.google.com/linux/chrome/deb/ stable main" ## refreshes the package lists sudo apt update ## install sudo apt install google-chrome-stableChromedriver
Select an appropriate Chrome driver base on the version of your Chrome browser. For more detailed information on this topic, please refer to this link for further insights.
## download the chromedriver wget https://chromedriver.storage.googleapis.com/113.0.5672.63/chromedriver_linux64.zip ## install unzip apt install unzip ## unzip it unzip chromedriver_linux64.zip ## move the chromedriver executable file to the /usr/bin directory sudo mv chromedriver /usr/bin/chromedriver ## change the ownership and group of the file /usr/bin/chromedriver to the root user sudo chown root:root /usr/bin/chromedriver ## make it executable sudo chmod +x /usr/bin/chromedriverInstall Python, Selenium Package, and Xvfb
Python Selenium is a powerful package used for automating web tasks, including browser automation and automated testing. We will be utilizing this package in our Python script. While Xvfb (X virtual framebuffer) is a virtual display server that allows running graphical applications without a physical display. It can be used in conjunction with Python Selenium to simulate a display environment for browser automation in a headless mode. By using Xvfb, you can perform automated web tasks without the need for a visible graphical interface.
## install python sudo apt-get install python3 python3-pip ## install selenium webdriver sudo pip3 install selenium sudo apt install xvfb
Configuring Jenkins
First, we add Jenkins to the list of sudoers by adding Jenkins ALL=(ALL) NOPASSWD:ALL at the end of the /etc/sudousers file.
Then on Jenkins UI, we install the ShiningPanda plugin to enable Python support in Jenkins. Additionally, we install the Xvfb Jenkins plugin, which allows running graphical applications in headless mode for UI testing. These plugins enhance Jenkins with Python capabilities and provide the necessary tools for executing GUI tests seamlessly.
To install the plugins in Jenkins, follow these steps:
Go to the Jenkins homepage and click on "Manage Jenkins" from the sidebar.
In the Manage Jenkins page, select "Manage Plugins."
In the "Available Plugins" tab, you can search for the desired plugins by typing their names in the search bar.
Locate the plugins and select the checkbox next to each plugin.
For each them, after you have selected the plugins click on the "Install without restart"
Configure Python and Xvfb installations by going to Manage Jenkins > Global Tool Configuration and search for the two, to tell Jenkins where Python and Xvfb installation is located. That can be gotten using
whereis python3
whereis xvfb-run

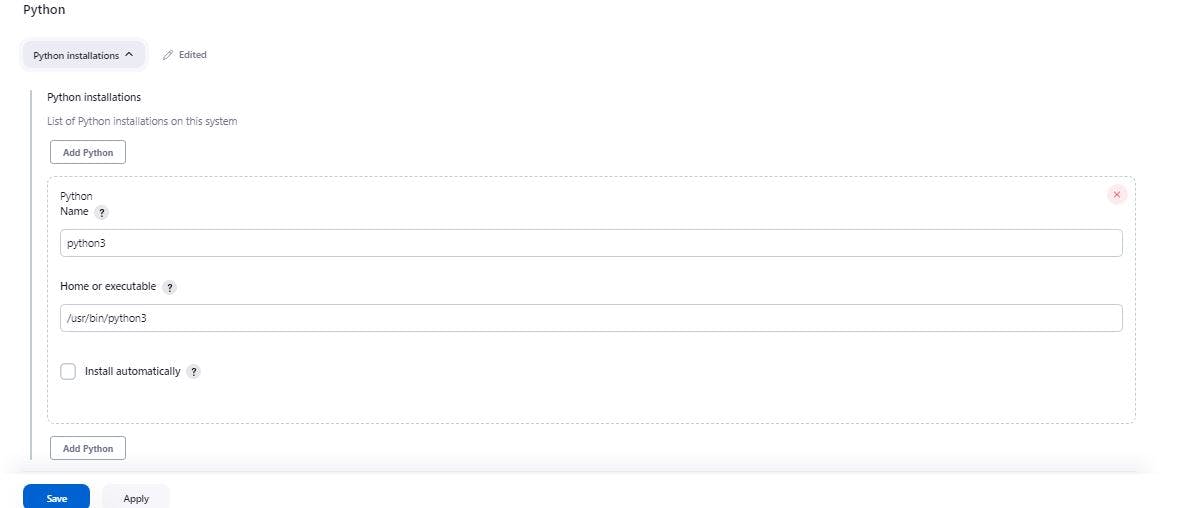
And be sure to click apply and save.
Executing the Test File on Jenkins
Here is my Python test script below.
import unittest
import collections
collections.Callable = collections.abc.Callable
from selenium import webdriver
from selenium.webdriver.chrome.options import Options
from selenium.webdriver.chrome.service import Service
from selenium.webdriver.common.by import By
from selenium.webdriver.support.ui import WebDriverWait
from selenium.webdriver.support import expected_conditions as EC
class test_ATGWorld(unittest.TestCase):
def setUp(self):
self.chrome_options = Options()
self.chrome_options.add_argument('--no-sandbox')
# self.chrome_options.add_argument('--headless')
self.chrome_options.add_argument('--disable-dev-shm-usage')
self.chrome_options.add_argument('--disable-gpu')
self.driver = webdriver.Chrome(service=Service('/usr/bin/chromedriver'), options=self.chrome_options)
def test_atg_website(self):
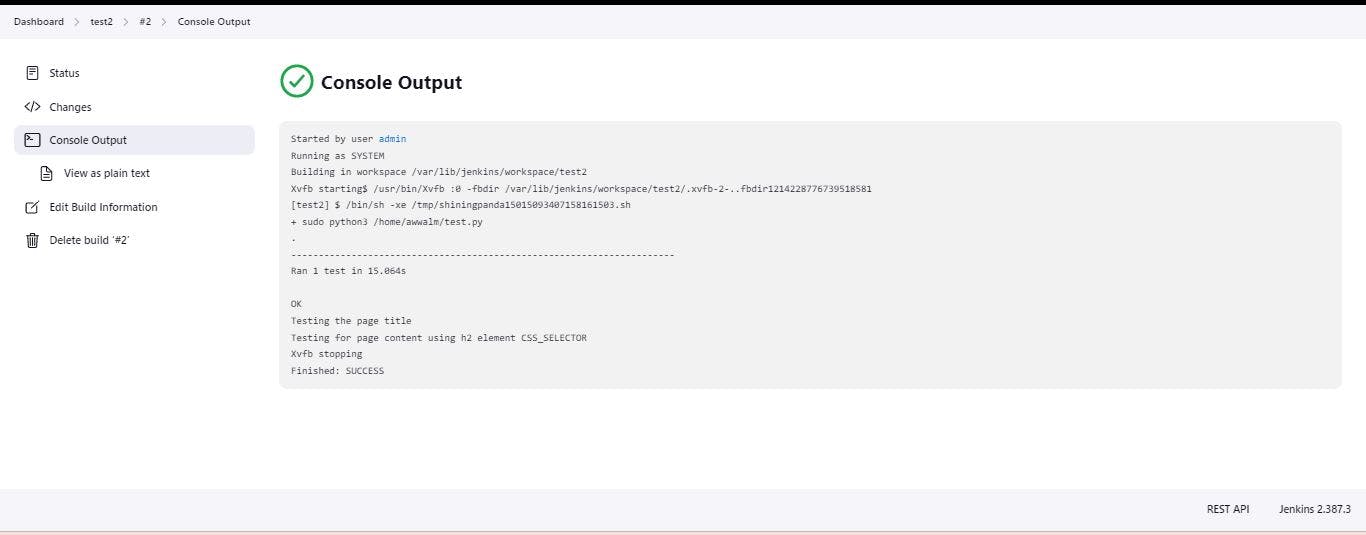
self.driver.get("https://atg.world/")
print('Testing the page title')
self.assertEqual(self.driver.title, "Across The Globe (ATG) - Professional and Personal Social Networking", 'wrong page title')
print("Testing for page content using h2 element CSS_SELECTOR")
self.assertTrue( WebDriverWait(self.driver, 10).until(
EC.presence_of_element_located((By.CSS_SELECTOR, "h2"))
), 'h2 element not present')
def tearDown(self):
self.driver.quit()
if __name__ == "__main__":
unittest.main()
Create a new item on Jenkins as a Freestyle project. Follow these steps:
Go to the Jenkins home page and click on "New Item" on the left-hand side of the screen.
Enter a name for the project and select "Freestyle project" as the project type.
Click on "OK" to proceed to the configuration page for the new project.
In the "Build Environment" section, enable the checkbox for "Start Xvfb before the build, and shut it down after." This sets up a virtual display for running graphical applications in headless mode.
In the "Build Steps" section, click on "Add build step" and select "Python Builder" from the dropdown menu.
In the "Command" field of the Python Builder, input the following command:
sudo python3 $Path_to_the_test_file- Replace
$Path_to_the_test_filewith the actual path to your test file.
- Replace
Click on "Save" to create the Jenkins project.
By following these steps, you will have created a new Jenkins item as a Freestyle project with the Xvfb display server started before the build, and the Python Builder configured to execute the specified Python test file using Python3.
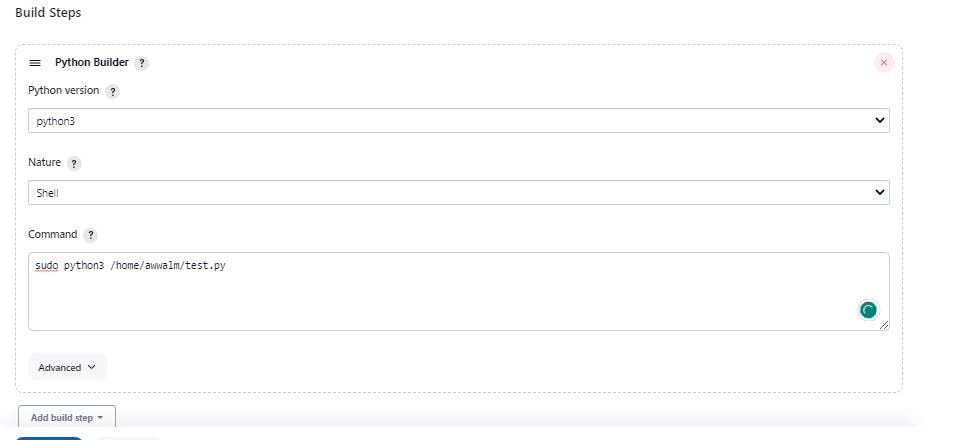
And build now,
Conclusion
In conclusion, this article provided a good guide on building a Jenkins Freestyle project for Python unit testing to verify website loading using the Selenium package. The process involved setting up a Jenkins job as a Freestyle project, configuring the necessary build environment, and executing Python unit tests using the Python Builder. If you have any feedback or questions, please feel free to leave a comment below.
